
Like us on Facebook
PLACE NAMES


 
|
|
Bretagne (Brittany) |
|
Brittany is a cultural region in the north-west of France. Previously a kingdom and then a duchy, Brittany was united to the Kingdom of France in 1532 as a province. Brittany has also been referred to as Less, Lesser or Little Britain (as opposed to Great Britain). Brittany is considered as one of the six Celtic nations.
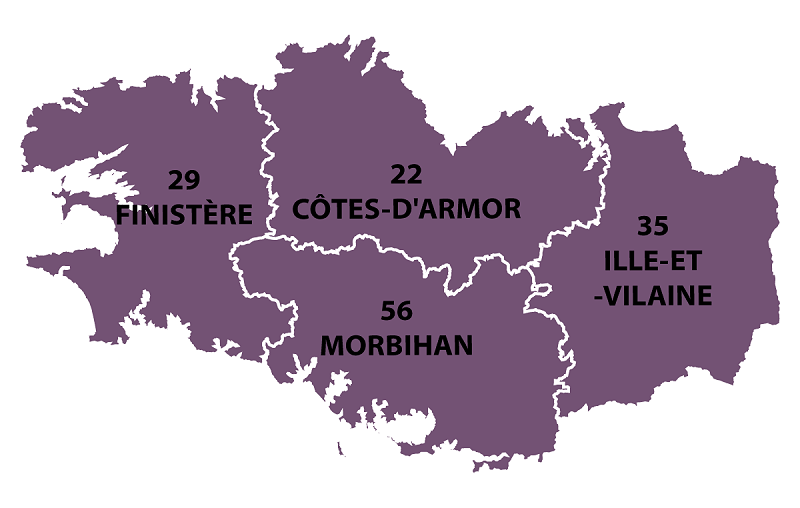
Brittany occupies the northwest peninsula of continental Europe in northwest France. It is bordered by the English Channel to the north, the Celtic Sea and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and the Bay of Biscay to the south. Its land area is 34,023 km² (13,136 sq mi). The historical province of Brittany is divided into five departments: Finistère in the west, Côtes-d'Armor in the north, Ille-et-Vilaine in the north east, Loire-Atlantique in the south east and Morbihan in the south on the Bay of Biscay.
In 1956, French regions were created by gathering departments among them. The Region of Brittany comprises, since then, four of the five Breton departments (80% of historical Brittany), while the remaining area of the old Brittany, the Loire-Atlantique department, around Nantes, forms part of the Pays de la Loire region. This territorial organisation is regularly contested. The Kingdom and the Duchy of Brittany, the province of Brittany, and the modern Region of Brittany cover the western part of Armorica, as it was known during the period of Roman occupation.
At the 2010 census, the population of historic Brittany was estimated to be 4,475,295. Of these, 71% lived in the region of Brittany, while 29% lived in the Loire-Atlantique department. In 2008, the largest metropolitan areas were Nantes (854,807 inhabitants), Rennes (654,478 inhabitants), and Brest (311,735 inhabitants).
Brittany is the largest French peninsula. The Breton coast is very indented, with many cliffs, rias and capes. The Gulf of Morbihan is a vast natural harbour with some forty islands that is almost a closed sea. In total, around 800 islands lie off the mainland; the largest being Belle Île, in the south. Brittany has over 2,860 km (1,780 mi) of coastline; it represents a third of the total French coastline.
The region is generally hilly because it corresponds to the western end of the Armorican massif, a very old range that also extends in Normandy and the Pays de la Loire region. Because of this continuity, the Breton border with the rest of France is not marked by any strong geographical landmark, apart from the river Couesnon, which separates Brittany from Normandy.
The Armorican massif reaches its maximal elevation outside of Brittany, in neighbouring Mayenne, at 417 m, and slopes towards the west before straightening on its western extremity, with the Montagnes Noires and the Monts d'Arrée. The highest hill in Brittany is the Roc'h Ruz in the Monts d'Arrée, at 385 m (1,263 ft). It is closely followed by several neighbouring hills culminating at around 384 m above sea level.
Coastal areas are usually named Armor or Arvor ("by the sea" in Breton), and the inland is called Argoat ("by the forest"). The best soils were primitively covered by large forests which had been progressively replaced by bocage during the Middle Ages. The Breton bocage, with its small fields enclosed by thick hedgerows, has almost disappeared since the 1960s to fit the modern agricultural needs and methods, particularly mechanisation.
Several forests still exist, such as the Paimpont forest, sometimes said to be the Arthurian Brocéliande. The poor and rocky areas are covered by large heathland and moorlands, and Brittany has several marshes, like the Brière, included in a Regional natural park. Another regional park encompasses the Monts d'Arrée and the Iroise seacoast. The Iroise Sea is also a UNESCO biosphere reserve.
The Breton peninsula appeared during the Cadomian Orogeny, which formed its northern coastline, between Guingamp and Fougères. The southern part emerged during the Hercynian orogeny. At the same time, an intense volcanic activity left large quantities of granite. Between the Cadomian and Hercynian periods, the region was submerged several times and the sea left fossils and sedimentary rocks, mostly schist and sandstone. Because of the absence of limestone, soils in Brittany are usually acid. The Armorican massif straightened and flattened several times during the formation of the Pyrenees and the Alps. Changes in sea levels and climate led to a strong erosion and to the formation of more sedimentary rocks. Metamorphism is responsible for the distinctive local blue schist and for the rich subsoil of the Groix island, which comprises glaucophane and epidote.
During the Quaternary glaciations, Brittany was covered by loess and rivers started to fill the valleys with alluvial deposits. The valleys themselves were a result of a strong tectonic activity between the African and the Eurasian plate. The present Breton landscape did not acquired its final shape before one million years ago. The Breton subsoil is characterised by a huge amount of fractures that form a large aquifer containing several millions square meters of water.
 Feel free to Email me any additions or corrections Feel free to Email me any additions or corrections
LINKS AVAILABLE TO YOUR SITE
| |
| |





